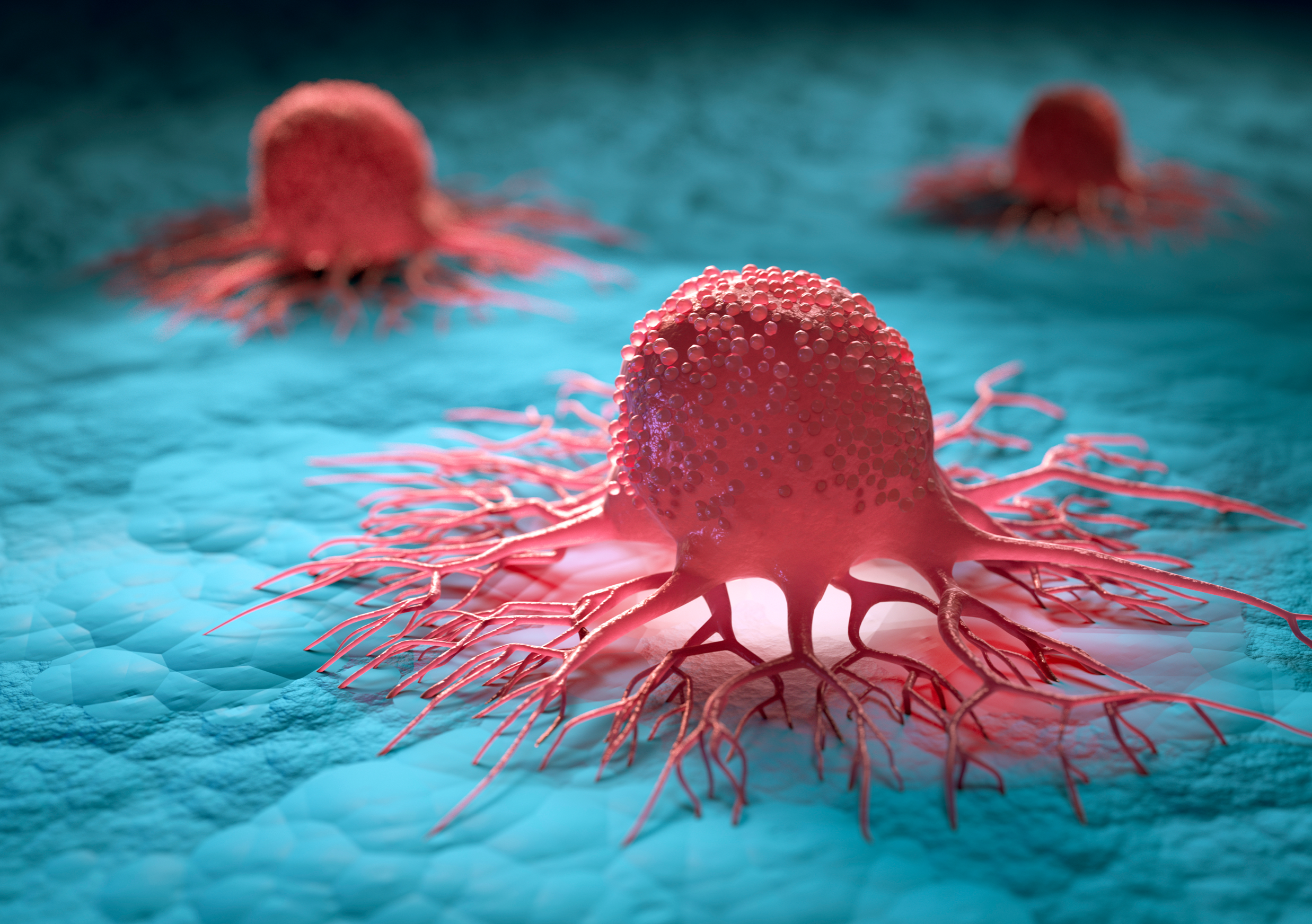
Bladder Cancer may be defined as the growth of abnormal tissues of tumor in the bladder lining spreading in the bladder muscle. Once diagnosed; it may be classified into two types; namely: the non-muscle invasive bladder cancer and muscle-invasive bladder cancer, while when it spreads to other parts of the body, then it is known as advanced or metastatic bladder cancer.
Causes of bladder cancer include for example but not limited to; tobacco, older age, exposure to chemicals such as amines, benzene products and aniline dyes, radiation therapy to the pelvic area, chronic tract infection and family history.
Bladder Cancer may be diagnosed through various tests and procedures, which include imaging CT tests, urogram or retrograde pyelogram, examination of urine sample to check for cancer cells, biopsy and cystoscopy to examine structures for signs of disease.
Symptoms of the diseases include blood in urine, pain or burning feeling during urination, frequent urination, feeling the need to urinate and lower back pain. While treatment includes surgery through transurethral resection, partial cystectomy or radical cystectomy with urinary diversion, radiation therapy using high energy rays of other types of radiation, chemotherapy to stop the growth of cancer cells, immunotherapy to help the immune system fight cancer, targeted therapy using drugs or other substances.
Prevention of bladder cancer may be through stopping smoking, eating a healthy diet, avoiding workplace chemicals and drinking plenty amounts of water.
The Department of Oncology at Al Salam Hospital consists of a team of specialists including medical oncologists, oncology nursing staff, social workers, dieticians and psycho-oncologists offering the best medical services to our patients according to the international accredited guidelines and standards. The Department offers comprehensive medical non-surgical treatment for patients with cancer, along with inpatient and outpatient chemotherapy and supportive and palliative care, in addition to providing care for hematological diseases by conducting the appropriate blood tests and bone marrow procedures for the correct diagnosis and up-to-date treatment.
References:
- National Cancer Institute, February 2023
- NHS
- Cleveland Clinic